Musculoskeletal Imaging / Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Imaging in Rheumatoid Arthritis
-

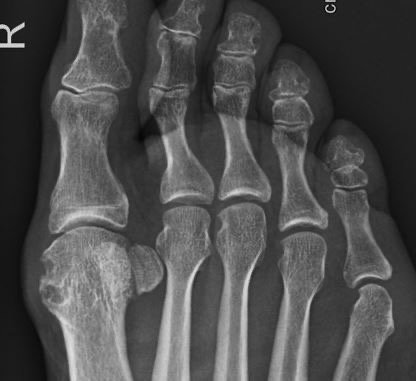
Radiography
Commonly radiography is used as a surrogate outcome for structural progression in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Different scoring methods are established for the quantification of radiographic progression. However, in several studies focusing on biological and target synthetic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs, these scores have not been able to differentiate radiographic progression in detail.
-

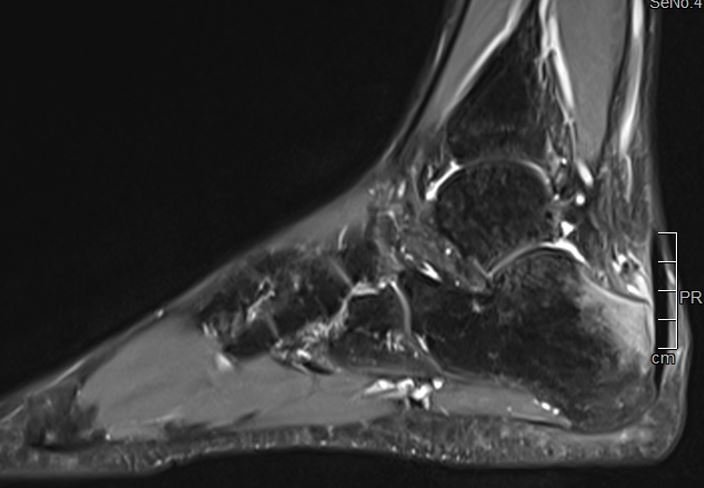
RAMRIS
In contrast, the RAMRIS [Outcome Measures in Rheumatology RA magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) Scoring system] has been used in clinical RA trials since 2002. RAMRIS evaluates bony erosion, bone marrow edema/osteitis, and synovitis, and is now the standard method of objectively quantifying inflammation and damage by MRI in RA trials. Longitudinal studies and clinical trials have documented RAMRIS variables to have face, construct, and criterion validity; high reliability and sensitivity to change; and the ability to discriminate between therapies. This has enabled RAMRIS to demonstrate inhibition of structural damage progression with fewer patients and shorter follow-up times than has been possible with conventional radiography. Technical improvements have facilitated development and validation of additional pathologies, i.e. joint space narrowing and tenosynovitis.
-

DCE-MRI
Dynamic Contrast Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging (DCE-MRI) is a method evaluating perfusion characteristics, which provides additional information for the diagnosis and therapy response of arthritic disease, e.g., research suggests DCE- MRI can confirm the clinical diagnosis of arthritis earlier than RAMRIS in some patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. We have been conducting RA trials using DCE-MRI and BICL experts offer DCE- MRI for the assessment of synovitis in RA.
-

BICL Services
BICL provides reading services for plain radiography and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) by expert readers, as well as imaging consultancy services for clinical trials and observational studies in the field of rheumatoid arthritis. Our readers are qualified and trained in scoring MRIs according to the Rheumatoid Arthritis MRI score (RAMRIS) for rheumatoid arthritis. They have been trained by Paul Bird, MD, University of New South Wales, first author of the established RAMRIS system and atlas and member of the OMERACT MRI in Arthritis Working Group. In addition, BICL offers quantification of inflammatory activity based on Dynamic Contrast Enhanced (DCE) MRI to measure the activity of synovitis over time to monitor treatment effects of novel pharmaceuticals that target specifically the synovium and the subchondral bone.”